Archives
- 2026-03
- 2026-02
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-07
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2019-06
- 2019-05
- 2019-04
- 2018-11
- 2018-10
- 2018-07
-
br Material and methods br Results
2022-11-05
Material and methods Results Discussion Although we were not able to detect 12/15-LOX mRNA in the lungs of 12/15-LOX knockout mice substantial amounts of 15-HETE could be detected in BALF. In fact, significant synthesis of 15-HETE in 12/15-LOX mice have been already reported [17]. The redun
-
For the time being fluorescent in situ hybridization
2022-11-05
For the time being, fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) remains the ‘gold standard’ for ALK rearrangements diagnosis but immunohistochemistry has become a widely used pre-screening tool and the FDA recently approved the Ventana ALK (D5F3) CDx Assay (Ventana Medical Systems, Tucson, AZ) as a com
-
Microbe derived ligands can also activate
2022-11-05
Microbe-derived ligands can also activate AHR. Malassezia, a commensal yeast in human skin, can metabolize tryptophan into several AHR activating compounds including FICZ and ICZ [59]. Lactobacillus converts tryptophan into indole-3-aldehyde (IAld), which can activate AHR and promote IL-22 productio
-
KT 5823 australia Exposure to B a P is an
2022-11-05
Exposure to B[a]P is an epidemiologically proven cause of lung cancer (Hecht, 2003; Rojas et al., 2004; Alexandrov et al., 2010), and the formation of B[a]PDE-N2-dG adducts is considered to be the critical event in lung tumorigenesis by B[a]P. On the other hand, there is evidence suggesting that the
-
According to their structures and substrate
2022-11-05
According to their structures and substrate specificity, MMPs are divided into five major groups: collagenases (e.g., MMP1), gelatinases (e.g., MMP2, MMP9), stromelysins (e.g., MMP3, MMP10), matrilysins (e.g., MMP7), and membrane-type MMPs [7]. Among them, MMP1 is a major collagenase that degrades t
-
br Detection and possible treatments for prostate
2022-11-05
Detection and possible treatments for prostate cancer PC can be diagnosed, by screening for prostate-specific antigen (PSA) and after diagnosis, treatments may include intense observation, radical prostatectomy, radiation, chemotherapy, hormone therapy or vaccination depending on the type and sta
-
Finally one can ask whether
2022-11-05
Finally, one can ask whether these results throw any light on the nature of the target in SNMG patients. Interestingly, the results of the in vitro incubations suggested that SNMG sera might increase AChR expression to a small extent, raising the possibility that SNMG patients, who have thymic chang
-
Melatonin synthesis Tacrine an aminoacridine derivative Fig
2022-11-05
Tacrine, an aminoacridine derivative (Fig. 1, A), was the first AChE inhibitor approved for treatment of AD [12], [13]. This compound was withdrawn from the market due to its hepatotoxicity [14]. In spite of tacrine's side effects, it is still an attractive lead compound for medicinal chemists due t
-
ACh induced changes in respiratory frequency could be of int
2022-11-05
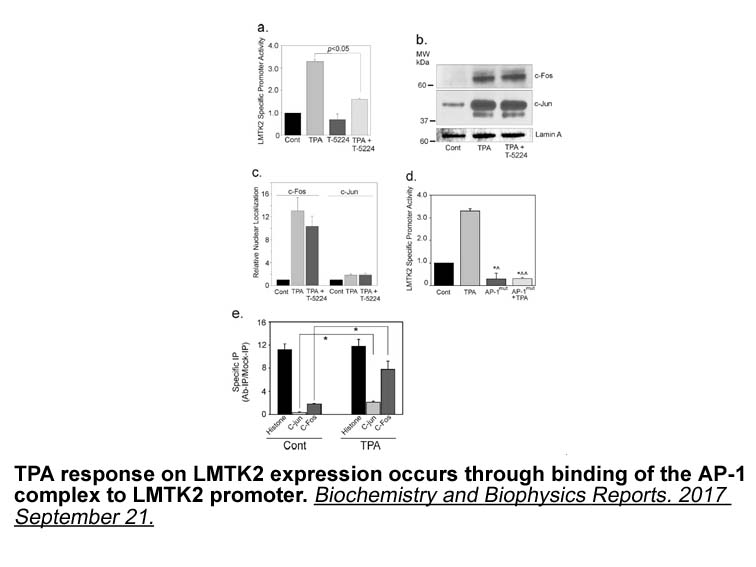
ACh-induced changes in respiratory frequency could be of interest. They may reveal an important mechanism of respiratory modulation at the caudal NTS level. ACh-induced increases in respiratory frequency within this region have been also reported by Furuya et al. (2014). Changes in respiratory timin
-
br Materials and methods br
2022-11-05
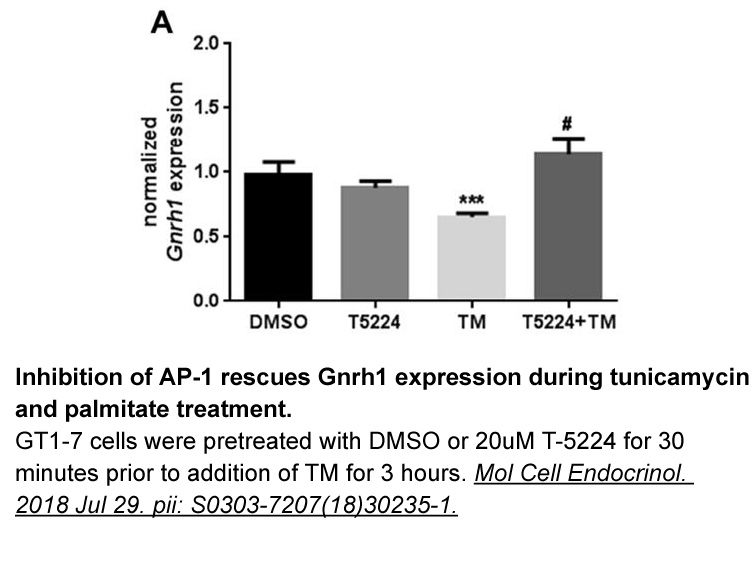
Materials and methods Results and discussions Conclusion Fermented camel milk with NS4 exhibited remarkable ACE-inhibitory activity, which revealed its potential application for the preparation of fermented camel milk beverage or fermented camel milk derived peptides in different foods or i
-
br Conclusions br Conflicts of interest
2022-11-05
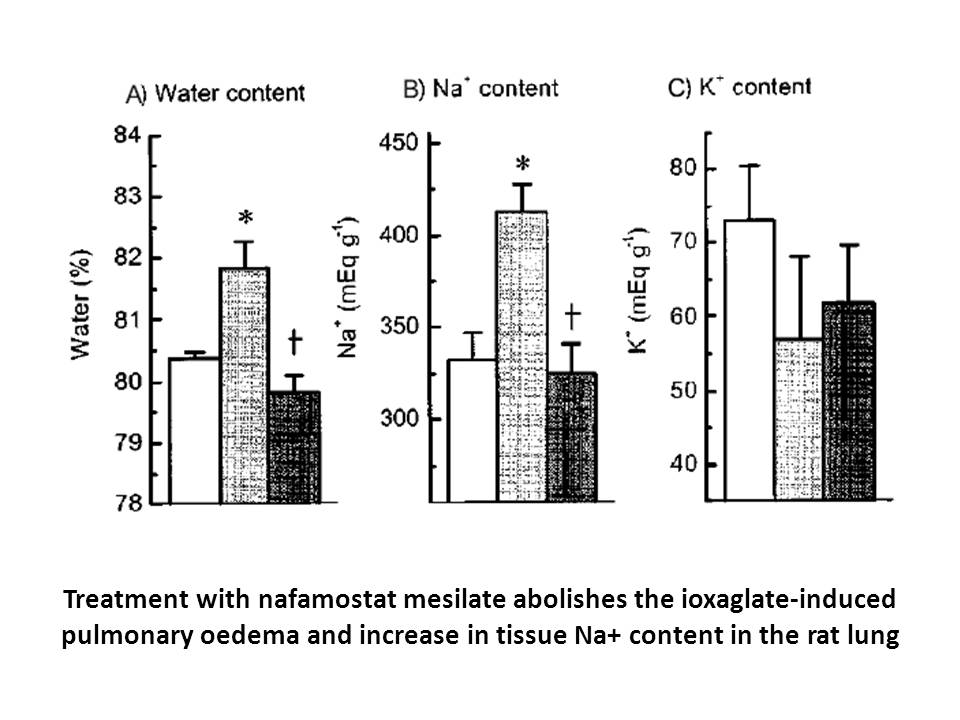
Conclusions Conflicts of interest Acknowledgements This work was supported by Ege University Research Fund [BAP, 14-ECZ-030, 2016]. Introduction The interest in the effects of endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) in the aquatic environment continues to increase over the past decade, sp
-
In an effort to determine if one ARI
2022-11-05

In an effort to determine if one 5ARI was more effective than the other, the Enlarged Prostate International Comparator Study (EPICS) [17] compared treatment with finasteride and dutasteride in 1630 men over the age of 50 and concluded that after one year of treatment, both groups had statistically
-
A variety of quinazoline or fused pyrimidine substituted dia
2022-11-05
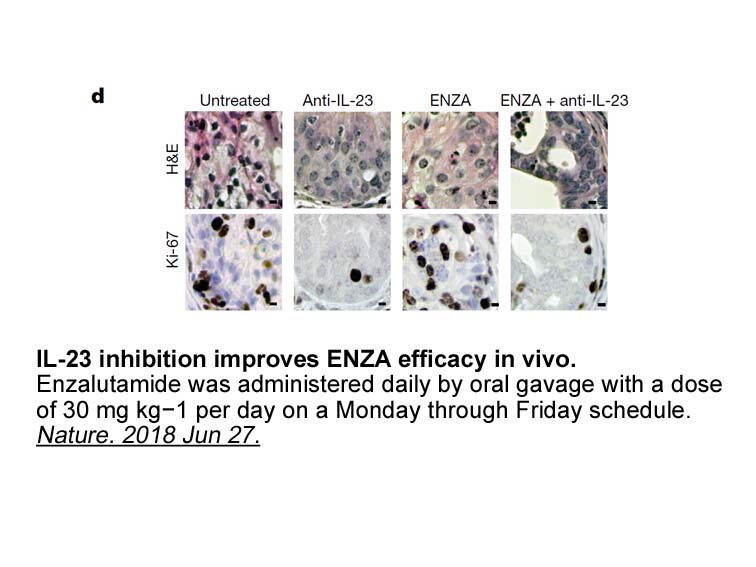
A variety of quinazoline or fused pyrimidine-substituted diaminotriazoles showed sub-100nM inhibition of Axl (). Diaminotriazoles similarly substituted with quinolines, isoquinolines and benzothiazoles also showed potent Axl activity (data not shown), but generally exhibited potent cytotoxicity and
-
br Dual role of autophagy in human diseases Emerging evidenc
2022-11-05
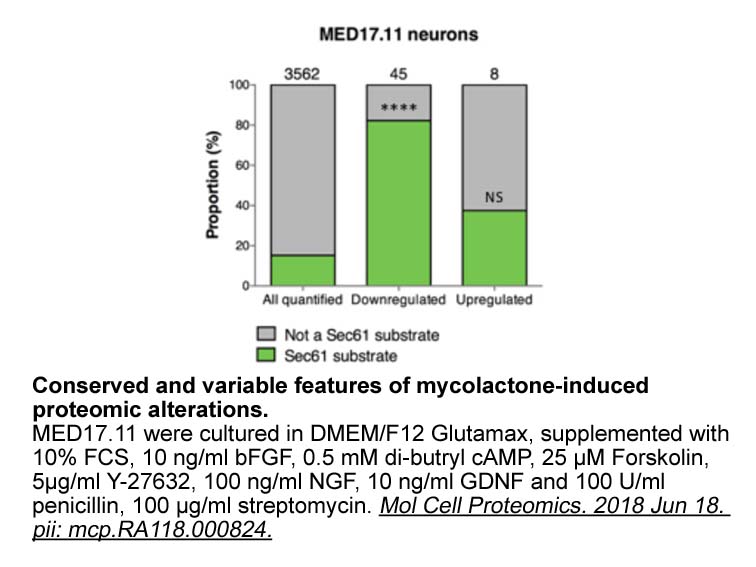
Dual role of autophagy in human diseases Emerging evidence suggests that autophagy serves as a double-edged sword in several human diseases, such as CNS diseases (Rubinsztein et al., 2015), arteriosclerosis (Schrijvers et al., 2011) and cancer (Ozpolat and Benbrook, 2015). Likewise, currently the
-
br Autophagy at the Synapse The
2022-11-05
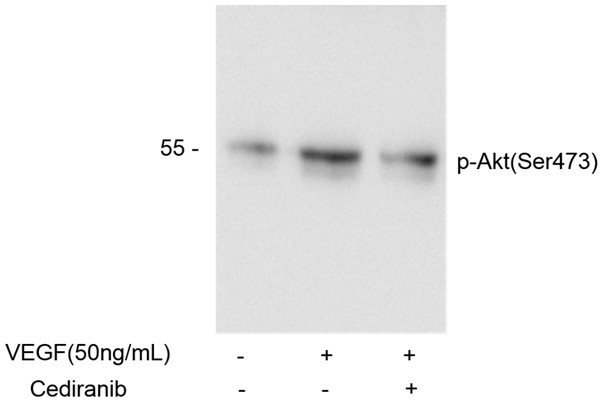
Autophagy at the Synapse The synapse is a highly specialized neuronal compartment that forms the basic unit of communication between neurons. Communication relies on electrical signals that are propagated down the axon of the presynaptic neuron, where they trigger the quantal release of neurotran
16565 records 392/1105 page Previous Next First page 上5页 391392393394395 下5页 Last page